Psych 101 offers engaging articles that explore the concepts, theories and practices of classic and contemporary psychology. Whether you are a student, a teacher or just curious, we hope you will enjoy reading our works.

Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
Explore the psychological, biological, and environmental factors contributing to SAD, along with its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.

Diffusion of Responsibility
Explore the intricacies of diffusion of responsibility, discussing its psychological underpinnings, historical context, and real-world implications, and criticisms, while also offering strategies to mitigate its effects.
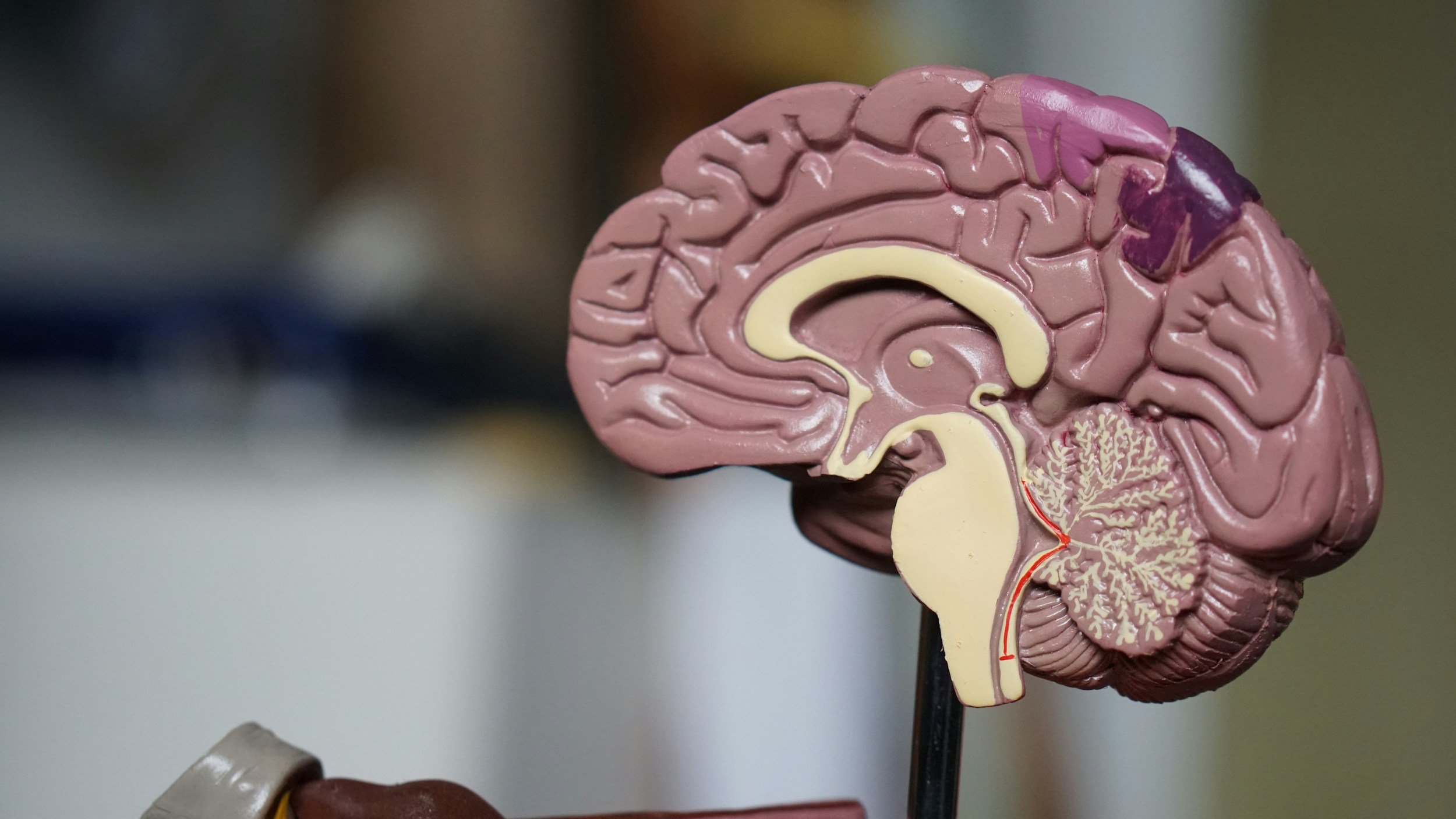
The Difference Between Grey and White Matter in the Human Brain
Explore the differences between grey and white matter, their roles in brain function, and their significance in neurological health and disease.

Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs: An Overview
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, introduced by Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A Theory of Human Motivation," is a foundational model in psychology that describes the stages of human development and motivation. This theory posits that human needs are arranged in a hierarchical order, starting from the most basic physiological needs to the highest level of self-actualization. Understanding this hierarchy provides valuable insights into human behaviour, motivation, and psychological well-being.

Exploring the Effectiveness of Flashcards for Learning and Retention
Delve into the psychological mechanisms behind flashcards, we evaluate their efficacy based on peer-reviewed research, and explore best practices for their use in various educational contexts.

Criticism of Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
By critically examining Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, we can appreciate its historical significance while also embracing more complex and culturally sensitive models of human motivation

Myers-Briggs Type Indicator: is it Scientific?
This article explores whether the MBTI has valid scientific support, drawing on peer-reviewed sources to evaluate its reliability, validity, and utility.

Freud's Psychoanalytic Theory Part 5: Exploring Psychoanalysis and Therapeutic Techniques
Sigmund Freud's psychoanalytic theory revolutionized the field of psychology by introducing the concept of psychoanalysis as a therapeutic approach. Psychoanalysis aims to explore the unconscious mind, uncover repressed memories and desires, and provide insights into the complexities of human behaviour. This article delves into Freud's psychoanalytic theory of psychoanalysis and examines its key therapeutic techniques and their implications for understanding psychological healing.

An Exploration of Freudian Defence Mechanisms
Explore Freud's theory of defence mechanisms in-depth and understand how the mind unconsciously protects itself from anxiety through repression, denial, projection, and more. A comprehensive guide to their psychological impact and relevance in modern therapy.

Freud's Psychoanalytic Theory: An Exploration of Psychosexual Development
Explore Freud’s five psychosexual stages—oral, anal, phallic, latency, and genital—uncover how they shape personality, and discover modern critiques and applications.

Freud’s Exploration of the Unconscious Mind: An Overview
Explore Freud's theories on the unconscious mind, including the topographical and structural models, defence mechanisms, and their impact on behaviour. A comprehensive guide to understanding Freud's exploration of the psyche.

A Guide to Freud's Structure of the Mind: Exploring the Id, Ego, and Superego
Explore Freud's theory of the id, ego, and superego with clear explanations and practical examples. Learn how these parts of the psyche shape behaviour and decision-making.

The Power of Operant Conditioning: Understanding Behaviour Modification
We explore the concept of operant conditioning, its key principles, real-world applications, and the underlying mechanisms that drive behaviour change.

Concepts: Classical Conditioning
This article aims to explore the concept of classical conditioning, its basic principles, prominent experiments, and its implications across various domains of psychology.

Review: Examining Richard Lazarus' Research on Cognitive, Social, and Physiological Determinants (1991)
This article aims to delve into Lazarus' study, summarizing its key concepts, research methods, findings, and the implications for our understanding of emotions.

Understanding Prejudice and Discrimination: A Review of Gordon Allport's "The Nature of Prejudice" (1954)
Explore Gordon Allport’s The Nature of Prejudice (1954)—a landmark book on prejudice, discrimination, stereotypes, and intergroup relations. Learn how his Contact Hypothesis and psychological insights continue to shape social psychology today.

Carl Rogers' Person-Centered Approach and the Therapeutic Relationship
Explore Carl Rogers' person-centered therapy and its transformative impact on the counselling relationship. Learn how the therapeutic relationship, grounded in empathy, genuineness, and unconditional positive regard, shapes effective therapist-client connections.

Summary: Values, Assumptions, and Practices: Assessing the Moral Implications of Psychological Discourse and Action (Isaac Prilleltensky, 1997)
Isaac Prilleltensky's seminal work, "Values, Assumptions, and Practices: Assessing the Moral Implications of Psychological Discourse and Action," published in 1997, explores the ethical dimensions of psychological theory and practice. Prilleltensky calls for a critical examination of the values, assumptions, and practices embedded within the field of psychology, challenging professionals to consider the moral implications of their work. This article provides an overview of Prilleltensky's key ideas, emphasizing the importance of ethical reflexivity and the need for psychology to promote social justice and well-being.

Paper Review: The Stanford Marshmallow Experiment: Insights into Delayed Gratification
In the late 1960s, a ground breaking psychological study known as the Stanford Marshmallow Experiment captured the attention of researchers and the public alike. Led by psychologist Walter Mischel at Stanford University, the experiment explored the concept of delayed gratification and its impact on individuals' long-term success. The findings of this iconic study shed light on self-control, willpower, and their implications for human behavior. This article will delve into the details of the Stanford Marshmallow Experiment and its enduring influence on psychology.

Paper Review: The Negative Side of Positive Psychology. B. S. Held 2004
In 2004, Barbara S. Held published an influential paper titled "The Negative Side of Positive Psychology." This thought-provoking article challenged some of the assumptions and limitations of the emerging field of positive psychology, which had gained significant attention and popularity at the time.
