Psychology 101
Psych 101 offers engaging articles that explore the concepts, theories and practices of classic and contemporary psychology. Whether you are a student, a teacher or just curious, we hope you will enjoy reading our works.

The Intricate Experience of Déjà Vu
Déjà vu, which translates to "already seen" in French, is a psychological phenomenon where an individual feels an overwhelming sense of familiarity with something that is objectively new

The Silent Intruder: Understanding Microsleep and Its Far-Reaching Impacts
Delve into the nature of microsleep, its triggers, consequences, and the importance of detecting and mitigating its risks.

The Cocktail Party Effect
The cocktail party effect showcases the brain's extraordinary ability to manage and make sense of complex auditory scenes.

Impact of The Bobo Doll Experiment
Explore the lasting impact of the experiment that aimed to unravel the mechanisms behind learned aggression and its transmission through imitation.

The Rebel Within: How Reverse Psychology Hacks Our Desire for Freedom
Explore the mechanisms behind reverse psychology, its application across different contexts, its efficacy, and the ethical considerations it raises.

The Enduring Appeal of Twin Studies in Psychology
Explore the reasons behind the enduring appeal of twin studies in psychology, delving into their methodological strengths, contributions to understanding heritability, and their role in unraveling the complexities of gene-environment interactions.

How Virtual Reality is Revolutionizing Psychiatric Treatment
VR technology, popularized by the gaming industry, is now making strides in treating a variety of psychiatric disorders, offering new hope to millions around the world.

Beyond Suggestion: A Scientific Look at Hypnosis and its Therapeutic Applications
Delve into the efficacy of hypnotism, exploring whether it works and is backed by empirical evidence

Beyond Labels and Expectations: A Critical Look at Normative Determinism
Explore the concept of normative determinism, examines the scientific evidence supporting or refuting it, and discusses its implications for understanding human behaviour and societal dynamics.

The Psychology of Laughter: Evolutionary Roots and Social Impacts
Delve into the evolutionary origins of laughter, its psychological mechanisms and its profound social impacts.

The Power of Authority: Insights from Milgram's 1963 Experiment
Delve into the psychological mechanisms of Milgram's (1963) findings, and how subsequent research has expanded our understanding of these critical aspect of human behaviour

Nature vs. Nurture: A 21st Century Update
We provide an updated perspective on the nature versus nurture debate, examining contemporary research and its implications for understanding human behaviour and development.

Attachment Theory: An In-Depth Exploration
Delve into the core concepts of attachment theory, examine different attachment styles, explore the implications for adult relationships, and review contemporary research findings.

Cognitive Dissonance: Understanding the Conflict Within
Cognitive dissonance describes the discomfort experienced when holding two or more conflicting cognitions (e.g., beliefs, attitudes, values, or behaviours).

Understanding WEIRD: Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich, and Democratic
Delves into the implications of the WEIRD bias in psychological research, examining its impact on the validity and generalizability of findings, and exploring ways to address these limitations.

Understanding Seasonal Affective Disorder (SAD)
Explore the psychological, biological, and environmental factors contributing to SAD, along with its symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.

Diffusion of Responsibility
Explore the intricacies of diffusion of responsibility, discussing its psychological underpinnings, historical context, and real-world implications, and criticisms, while also offering strategies to mitigate its effects.
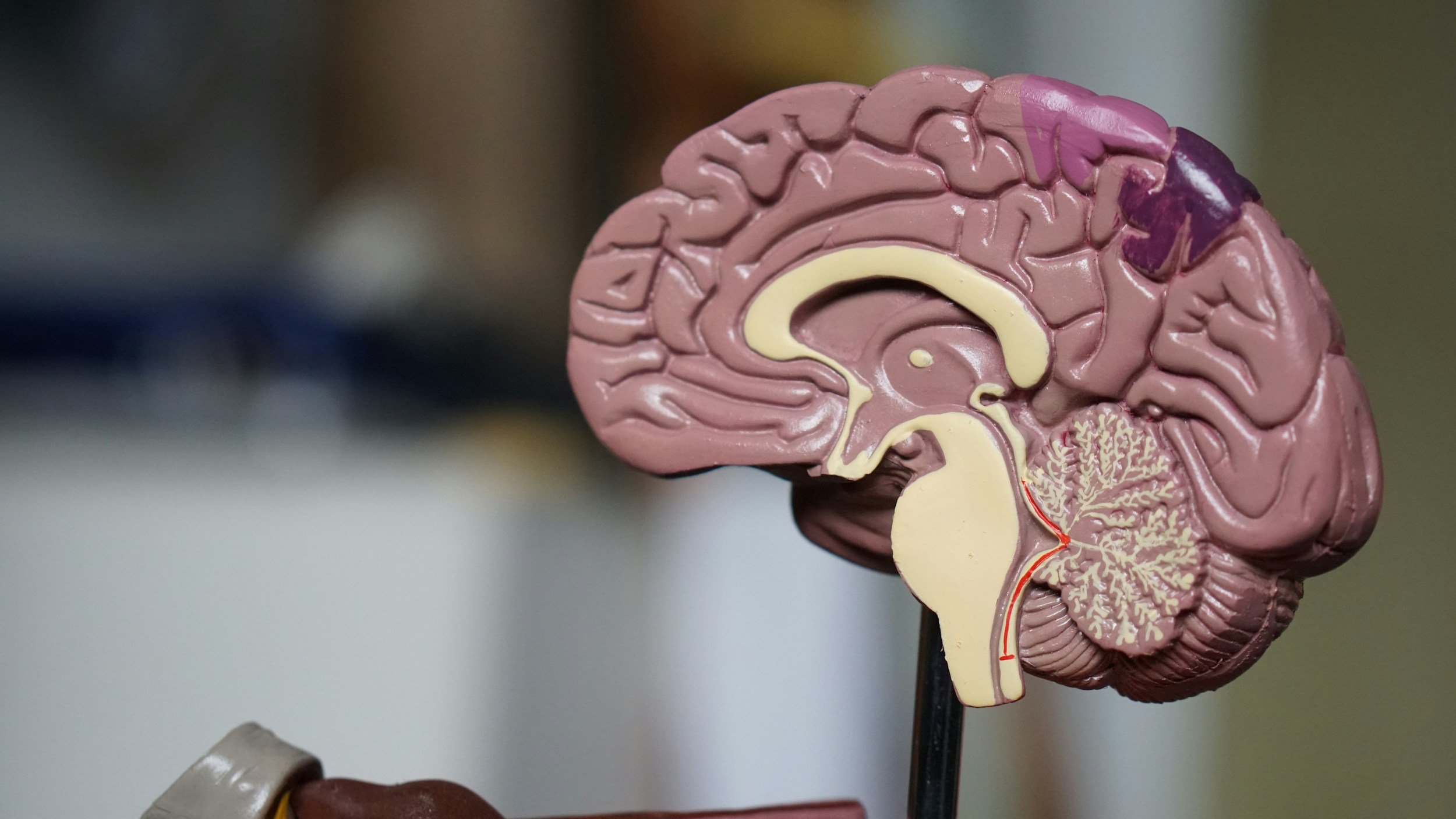
The Difference Between Grey and White Matter in the Human Brain
Explore the differences between grey and white matter, their roles in brain function, and their significance in neurological health and disease.

Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs, introduced by Abraham Maslow in his 1943 paper "A Theory of Human Motivation," is a foundational model in psychology that describes the stages of human development and motivation. This theory posits that human needs are arranged in a hierarchical order, starting from the most basic physiological needs to the highest level of self-actualization. Understanding this hierarchy provides valuable insights into human behaviour, motivation, and psychological well-being.




















